- Categories:
File functions (AI Functions)
PARSE_DOCUMENT (SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX)¶
Note
AI_PARSE_DOCUMENT is the latest version of this function. Use AI_PARSE_DOCUMENT for the latest functionality. You can continue to use PARSE_DOCUMENT (SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX).
Returns the extracted content from a document on a Snowflake stage as a JSON-formatted string. This function supports two types of extraction, Optical Character Recognition (OCR), and layout. For more information, see Parsing documents with AI_PARSE_DOCUMENT.
Syntax¶
SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX.PARSE_DOCUMENT( '@<stage>', '<path>', [ <options> ] )
Arguments¶
Required:
stageName of the Snowflake stage.
pathRelative path to the document on the Snowflake stage.
Optional:
optionsAn OBJECT value that contains options for parsing documents. The supported keys are shown below. All are optional.
'mode': Specifies the parsing mode. The supported modes are:'OCR': The function extracts text only. This is the default mode.'LAYOUT': The function extracts layout as well as text, including structural content such as tables.
'page_split': If set to TRUE, the function splits the output of the function to return content per page. Only PDF, PowerPoint (.pptx), and Word (.docx) documents are supported. Documents in other formats return an error. The default is FALSE.
Returns¶
A JSON object (as a string) that contains the extracted data and associated metadata. The options argument
determines the structure of the returned object.
Tip
To use the output in SQL, convert it to an OBJECT value using the PARSE_JSON function.
If the 'page_split' option is set, the output has the following structure:
"pages": An array of JSON objects, each containing text extracted from the document. If the document has only one page, the output still contains a"pages"array (which contains a single object). Each page has the following fields:
"content": Plain text (in OCR mode) or Markdown-formatted text (in LAYOUT mode).
"index": The page index in the file, starting at 0. Page numbers and formats specified in the document are ignored.
"errorInformation": Contains error information if document can’t be parsed.
"metadata": Contains metadata about the document, such as page count.Note
The
"pages"and"metadata"fields are present in the output when parsing succeeds."errorInformation"is present only if parsing fails.
If 'page_split' is FALSE or is not present, the output has the following structure:
"content": Plain text (in OCR mode) or Markdown-formatted text (in LAYOUT mode).
"errorInformation": Contains error information if the document can’t be parsed.
"metadata": Contains metadata about the document, such as page count.Note
The
"content"and"metadata"fields are present in the output when parsing succeeds."errorInformation"is present only if parsing fails.
Examples¶
OCR mode¶
SELECT TO_VARCHAR(
SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX.PARSE_DOCUMENT(
'@PARSE_DOCUMENT.DEMO.documents',
'document_1.pdf',
{'mode': 'OCR'})
) AS OCR;
Output:
{
"content": "content of the document"
}
LAYOUT mode¶
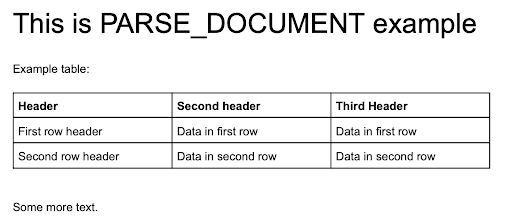
This example parses a document with a table shown in the following screenshot:
SELECT
TO_VARCHAR (
SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX.PARSE_DOCUMENT (
'@PARSE_DOCUMENT.DEMO.documents',
'document_1.pdf',
{'mode': 'LAYOUT'} ) ) AS LAYOUT;
Output:
{
"content": "# This is PARSE DOCUMENT example
Example table:
|Header|Second header|Third Header|
|:---:|:---:|:---:|
|First row header|Data in first row|Data in first row|
|Second row header|Data in second row|Data in second row|
Some more text."
}
Split pages¶
This example splits a multi-page document into separate pages, which are processed separately using the 'OCR' mode.
SELECT
TO_VARCHAR (
SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX.PARSE_DOCUMENT (
'@PARSE_DOCUMENT.DEMO.documents',
'document_1.pdf',
{'mode': 'OCR', 'page_split': TRUE} ) ) AS MULTIPAGE;
Output:
{
"pages": [
{
"content": "content of the first page",
"index": 0
},
{
"content": "content of the second page",
"index": 1
},
{
"content": "content of the third page",
"index": 2
}
],
"metadata": {
"pageCount": 3
}
}
Limitations¶
Snowflake Cortex functions do not support dynamic tables.