AI code conversion with source-system verification¶
AI code conversion with source-system verification improves the accuracy of the conversion process. It runs the generated test case against both the converted code in Snowflake and the original source code in the source database. It then checks that both the source code and the converted code produce equivalent results.
Compared to the default AI code conversion where SnowConvert only verifies that the converted code is running successfully on Snowflake, AI code conversion with source-system verification ensures functional parity, higher confidence, and overall better conversion quality.
AI code conversion with source-system verification is currently available for SQL Server databases. |
|---|
Overview of AI code conversion with source-system verification¶
AI code conversion with source-system verification currently requires an instance of SQL Server hosted in Snowpark Container Services (SPCS). This SQL Server instance acts as a host for the test cases that will be executed by the source-system verification process. The test results from this instance will be used as a baseline to compare against the test results generated by executing the test cases on the converted Snowflake SQL code.
Prerequisites for AI code conversion with source-system verification¶
An instance of SQL Server should be running in your SPCS environment. Download and run this shell script (https://snowconvert.snowflake.com/storage/linux/prod/scripts/push_mssql_server.sh) to deploy an instance of SQL Server in the SPCS environment.
Understand and agree to the legal responsibilities of using AI code conversion with source-system verification on your source data platform code inside the SPCS environment.
Create a custom specification file (for example,
spec.yaml). This file contains the connection parameters for the SQL Server instance running inside SPCS.Sample for
spec.yamlmode: "TWO_SIDED" source_test_database: connection_params: hostname: "mssql-server-demo-service.n4yw.svc.spcs.internal" port: 1433 username: "sa" password: "StrongPassw0rd" connection_metadata: type: "SPCS" spcs_service: name: "MSSQL_SERVER_DEMO_SERVICE" database: "SNOWCONVERT_AI" schema: "PUBLIC"
The mode “TWO_SIDED” indicates that the AI code conversion with source-system verification process will run on both source database code and target database code.
The host name, port number, and credentials for the SQL Server database running in SPCS is specified under
source\_test\_database.The name of the container service, database name and the schema name where the test cases for the source will be executed is specified under
connection\_metadata.
Steps to run AI code conversion with source-system verification¶
From the AI code conversion page, connect to Snowflake using a valid connection string. SnowConvert currently supports programmatic access tokens, in addition to the standard authentication methods for AI verification.
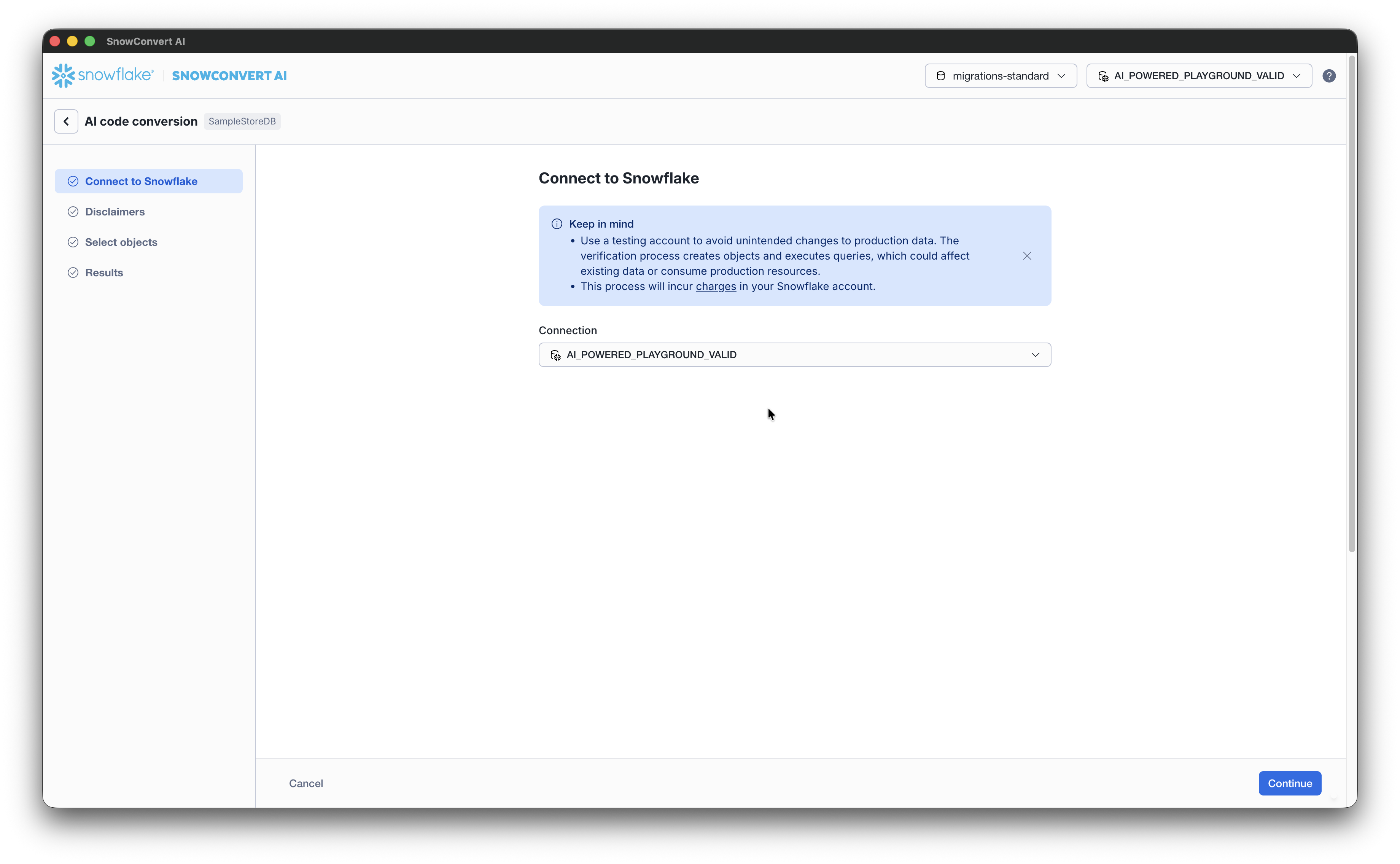
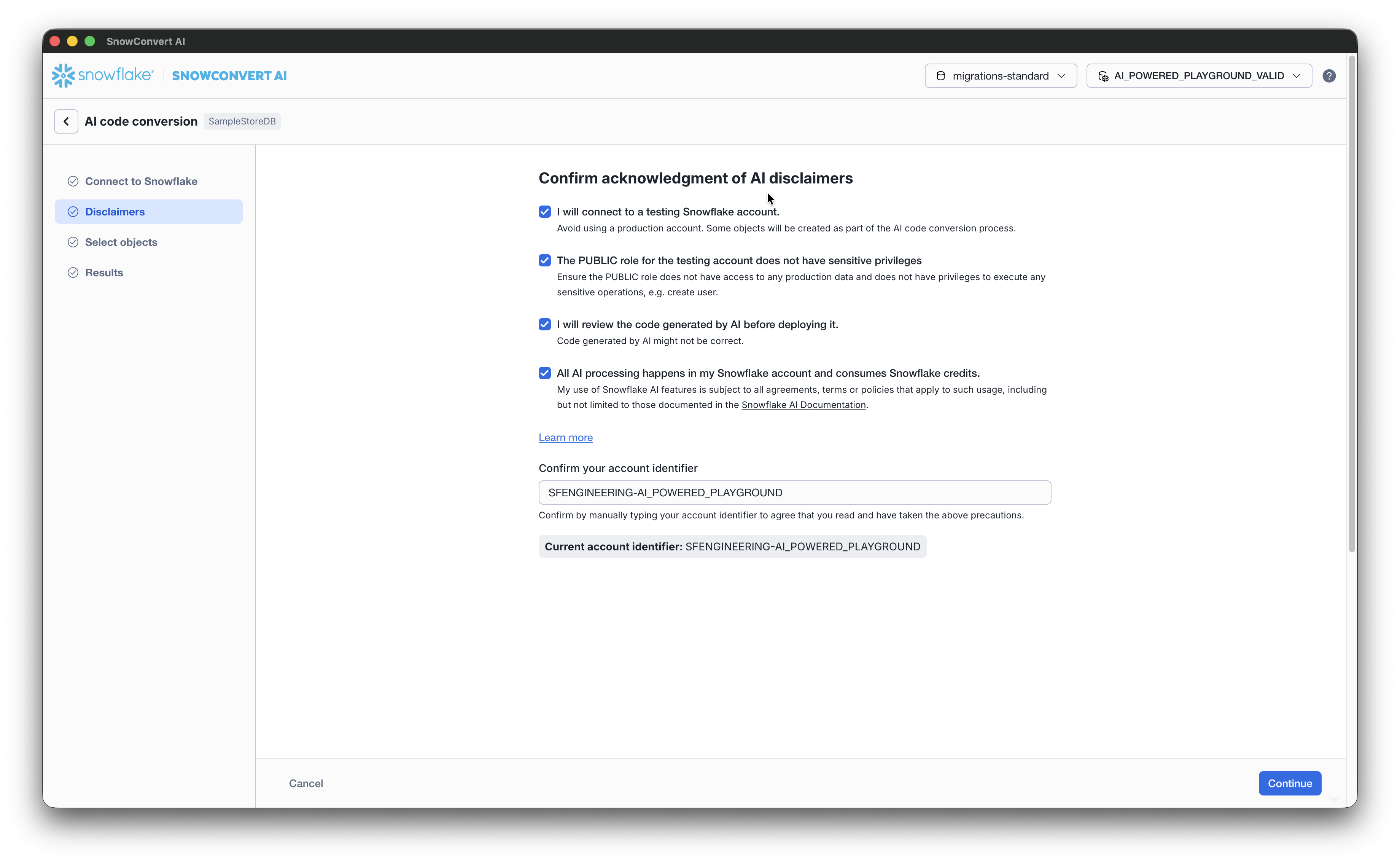
Accept the disclaimers and confirm your account identifier. Select Continue to proceed to the Select objects to verify with AI.
Select Upload custom instructions on the top left of the Select objects page.
Select the latest version of the
yamlfile you created as a prerequisite and select Save.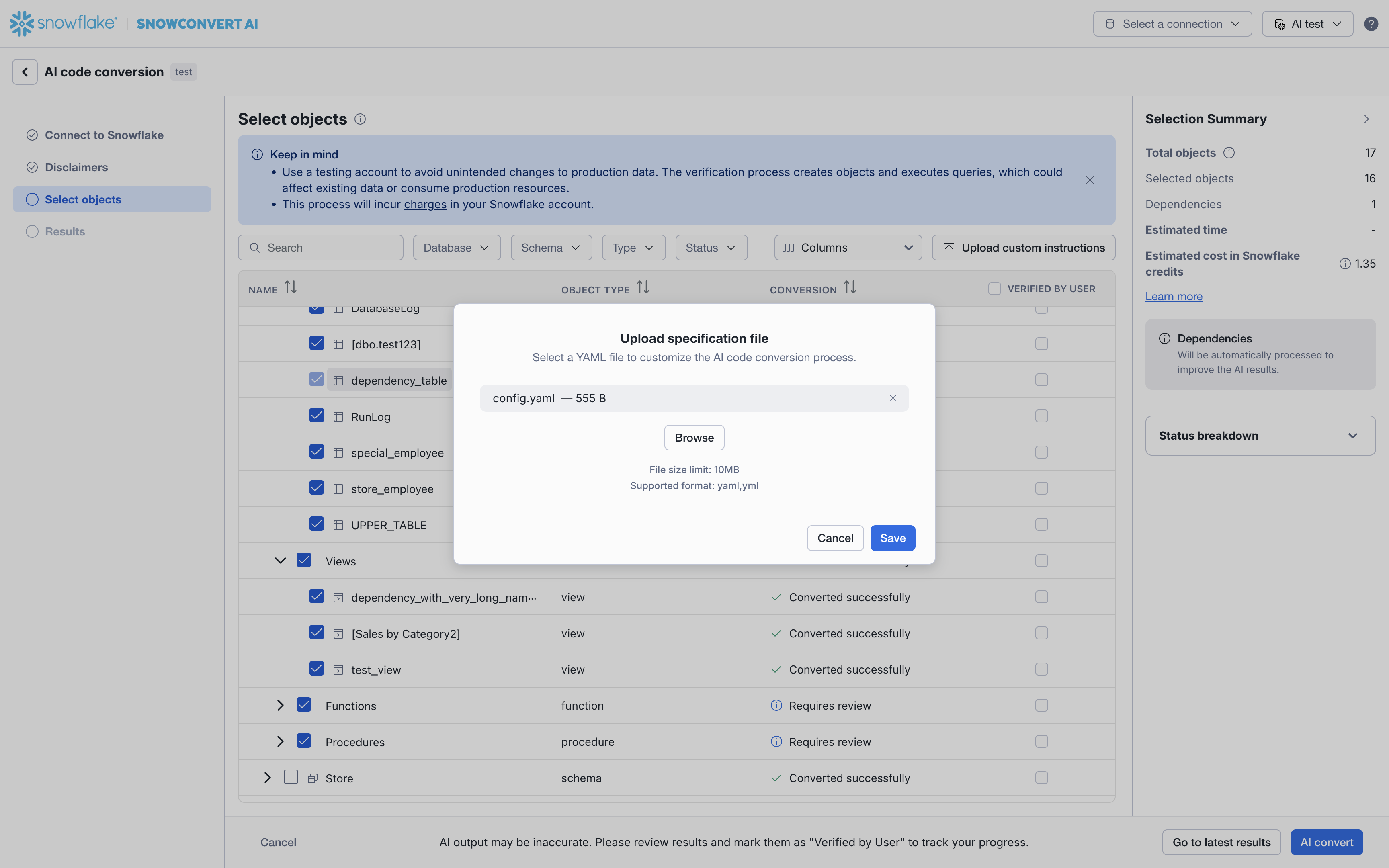
You have now configured the AI code conversion process to run in two-sided mode. This will compare test results from the source SQL Server database to the converted Snowflake SQL code.
Proceed with the AI code conversion steps to complete the source-system verification process.
Impact on costs and dependencies¶
The costs for running AI code conversion with source-system verification may be different from the default AI code conversion, depending on your Snowflake credits consumption for SPCS and Cortex AI. A summary of the estimated costs and number of objects affected by the source-system verification process can be found in the Selection Summary. We recommend reviewing the Selection Summary before proceeding to AI convert.