Creating a Snowflake Postgres Instance¶
Overview¶
You can create Snowflake Postgres instances by using either Snowsight or by executing Snowflake SQL statements. You can configure the size of the instance, the storage size, and the Postgres major version when creating an instance. You can also apply network policies to instances at creation time.
Privileges¶
To create Snowflake Postgres instances, you must use a role that has been granted the CREATE POSTGRES INSTANCE privilege on the account. By default, this privilege is granted to the ACCOUNTADMIN role.
To grant this privilege to other roles, a user with the ACCOUNTADMIN role can run the GRANT <privileges> … TO ROLE command:
GRANT CREATE POSTGRES INSTANCE ON ACCOUNT TO your_role;
Creating a Postgres instance¶
You can create a Postgres instance by using the Create menu or by using the Create button in the Postgres Instances page.
Using the main Create menu:
Select Postgres Instance.
Configure your instance.
Select Create.
Using the Create button on the Postgres instances page:
In the navigation menu, select Postgres.
In the Postgres Instances page, select the Create button at the top right.
Choose your instance configuration.
Select Create.
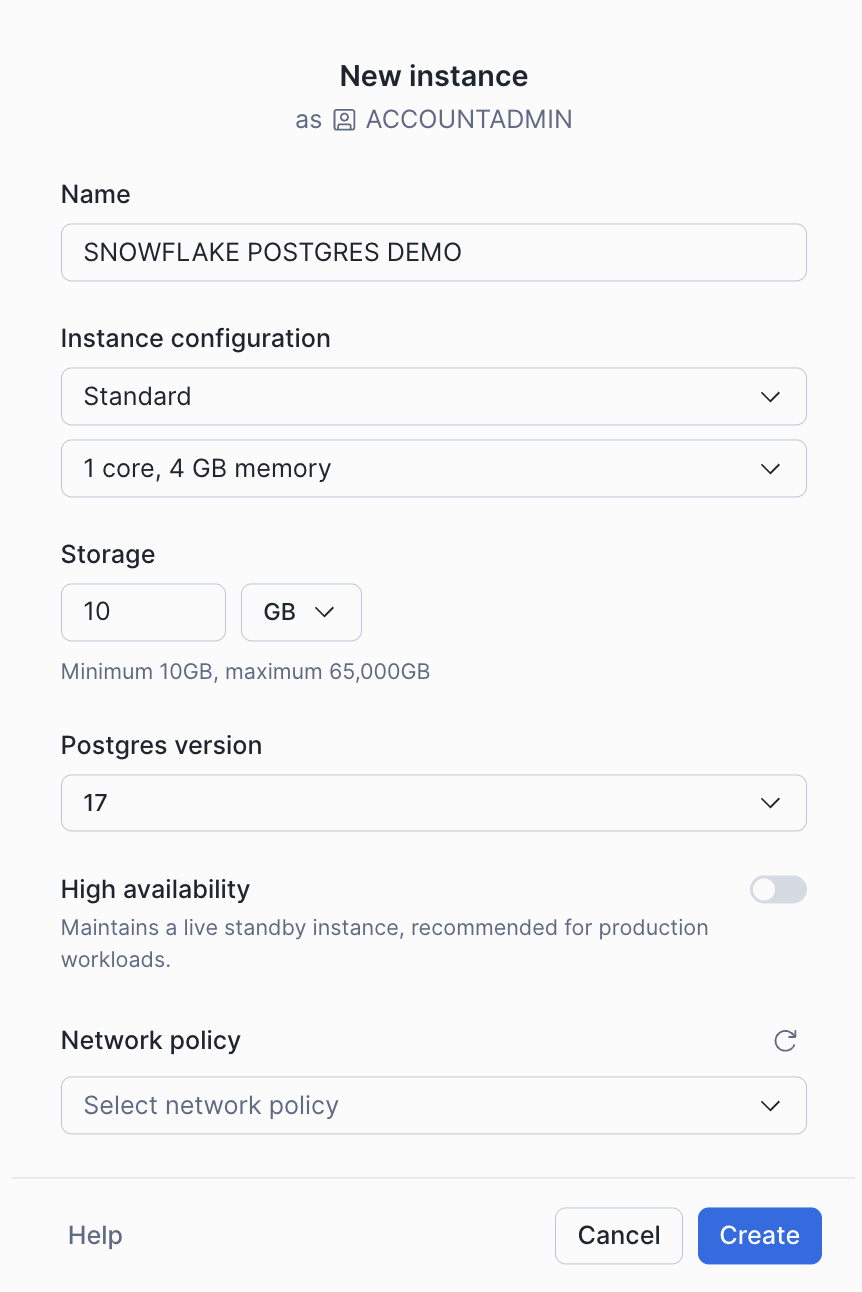
When you create an instance, the connection details are displayed, including the hostname and credentials needed to connect to the instance. Save these credentials in a secure location; they will not be shown again. You can regenerate credentials later if needed.
If you did not select a network policy, you will have the option to configure network settings from the instance details page. See Snowflake Postgres networking for more details.
Use the CREATE POSTGRES INSTANCE command to create a new Postgres instance. The syntax of this command is shown below:
CREATE POSTGRES INSTANCE <name>
COMPUTE_FAMILY = '<compute_family>'
STORAGE_SIZE_GB = <storage_gb>
AUTHENTICATION_AUTHORITY = POSTGRES
[ POSTGRES_VERSION = { 16 | 17 } ]
[ NETWORK_POLICY = '<network_policy>' ]
[ HIGH_AVAILABILITY = { TRUE | FALSE } ]
[ POSTGRES_SETTINGS = '<json_string>' ]
[ COMMENT = '<string_literal>' ];
For the command parameters:
COMPUTE_FAMILY = compute_familySpecifies the name of an instance size from the Snowflake Postgres Instance Sizes tables.
STORAGE_SIZE_GB = storage_gbSpecifies storage size in GB. Must be between 10 and 65,535.
AUTHENTICATION_AUTHORITY = POSTGRESDetermines how you authenticate to your instance. Currently, the only available option is
POSTGRES, but other authentication methods, includingSNOWFLAKE, might be supported in the future.POSTGRES_VERSION = { 16 | 17 | 18 }Specifies the version of Postgres to use.
Default: The latest Postgres version.
NETWORK_POLICY = 'network_policy'Specifies the network policy to use for the instance. To specify this parameter, you must have been granted the USAGE privilege on the NETWORK_POLICY object.
Default: No network policy is applied. A network policy will need to be configured before the instance can be reached. See Snowflake Postgres networking for more information.
HIGH_AVAILABILITY = { TRUE | FALSE }Specifies whether to enable high availability for the instance.
Default:
FALSEPOSTGRES_SETTINGS = 'json_string'Allows you to optionally set Postgres configuration parameters on your instance in JSON format. See Snowflake Postgres Server Settings for a list of available Postgres parameters.
'{"component:name" = "value", ...}'Default: No custom Postgres configuration parameters are set.
COMMENT = 'string_literal'Specifies a comment for the Postgres instance.
Default:
NULL
When you create the instance, one row with the following columns is returned:
statushostaccess_rolesdefault_database
The access_roles column contains the user name and password for both the snowflake_admin and application roles. Save these details in a secure location because they cannot be retrieved later.
Creating a new instance takes some time to complete. The instance displays its current state as it is building. See the list of instance states for details about the states that you see while instances are being created.