Cortex AI Functions: Images¶
With Cortex AI Images, you can accomplish the following:
Compare images
Caption images
Classify images
Extract entities from images
Generate embedding vectors for use in retrieval systems
Answer questions using data in graphs and charts
You can do those tasks with the following functions:
Input requirements¶
COMPLETE Multimodal can process images with the following characteristics:
Requirement |
Value |
|---|---|
Filename extensions |
|
Stage encryption |
Server-side encryption |
Data type |
Note
Processing files from stages is currently incompatible with custom network policies.
Analyze images¶
The COMPLETE function processes a single image or multiple images (for example, extracting differences in entities across various images) stored in a stage. See Create stage for media files for information on creating a suitable stage.
The function call specifies the following:
The multimodal model to be used
A prompt
The stage path of the image file(s) via a FILE object
Vision Q&A example¶
The following example uses Anthropic’s Claude Sonnet 3.5 model to summarize a pie chart science-employment-slide.jpeg stored in the @myimages stage.
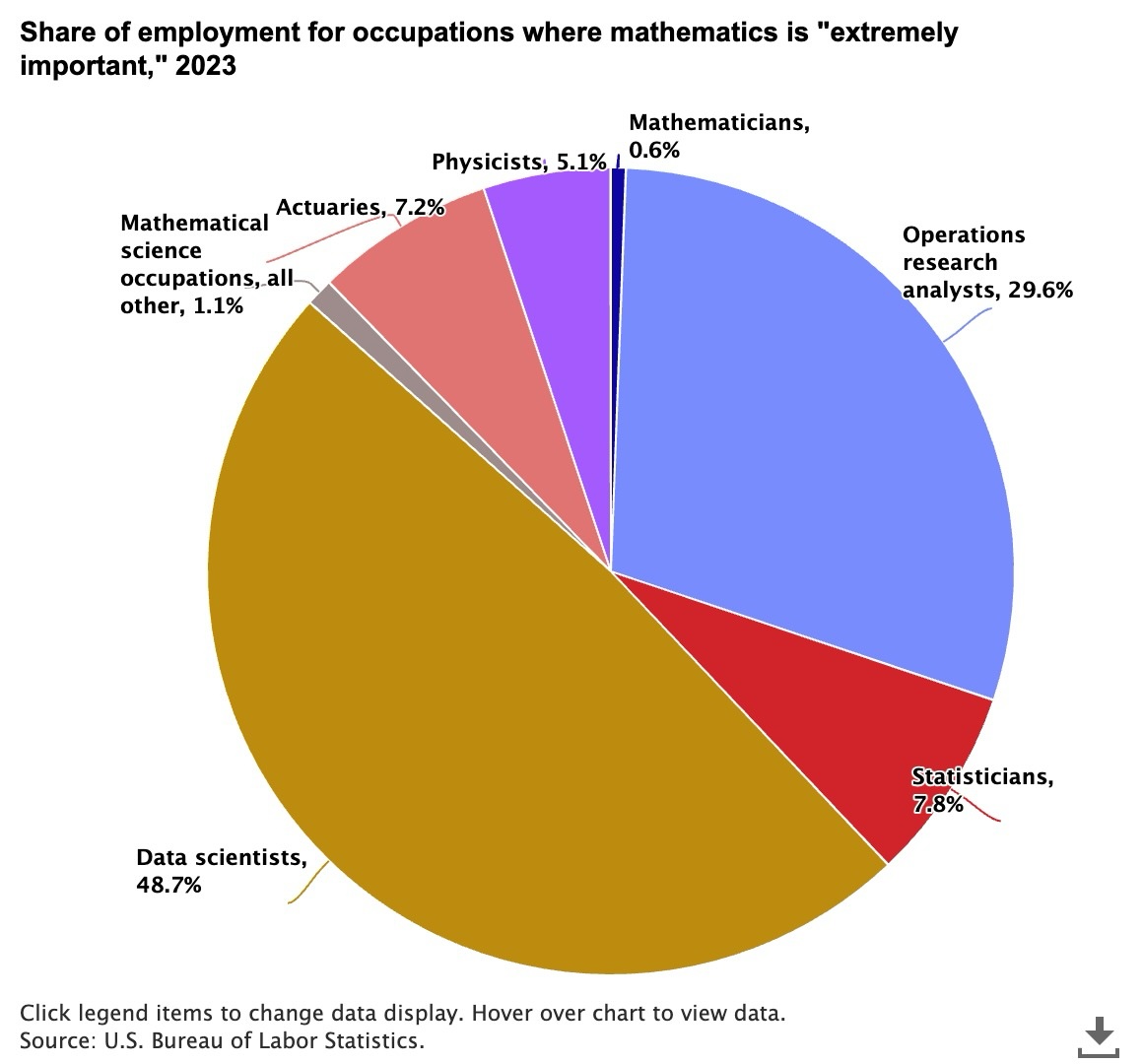
The distribution of occupations where mathematics is considered “extremely important” in 2023¶
SELECT AI_COMPLETE('claude-3-5-sonnet',
'Summarize the insights from this pie chart in 100 words',
TO_FILE('@myimages', 'science-employment-slide.jpeg'));
Response:
This pie chart shows the distribution of occupations where mathematics is considered "extremely important" in 2023.
Data scientists dominate with nearly half (48.7%) of all such positions, followed by operations research analysts
at 29.6%. The remaining positions are distributed among statisticians (7.8%), actuaries (7.2%), physicists (5.1%),
mathematicians (0.6%), and other mathematical science occupations (1.1%). This distribution highlights the growing
importance of data science in mathematics-intensive careers, while traditional mathematics roles represent a smaller
share of the workforce.
Compare images example¶
Note
Currently, only Anthropic (claude) and Meta (llama) models can reference multiple images in a single prompt.
Multiple image support for other models may be available in a future release.
Use the PROMPT helper function to process multiple images in a single COMPLETE call. The following example uses
Anthropic’s Claude Sonnet 3.5 model to compare two different ad creatives from the @myimages stage.

Image of two ads for electric cars¶
SELECT AI_COMPLETE('claude-3-5-sonnet',
PROMPT('Compare this image {0} to this image {1} and describe the ideal audience for each in two concise bullets no longer than 10 words',
TO_FILE('@myimages', 'adcreative_1.png'),
TO_FILE('@myimages', 'adcreative_2.png')
));
Response:
First image ("Discover a New Energy"):
• Conservative luxury SUV buyers seeking a subtle transition to electrification
Second image ("Electrify Your Drive"):
• Young, tech-savvy urbanites attracted to bold, progressive automotive design
Classify images example¶
The following example uses AI_CLASSIFY to classify an image for a real estate application.
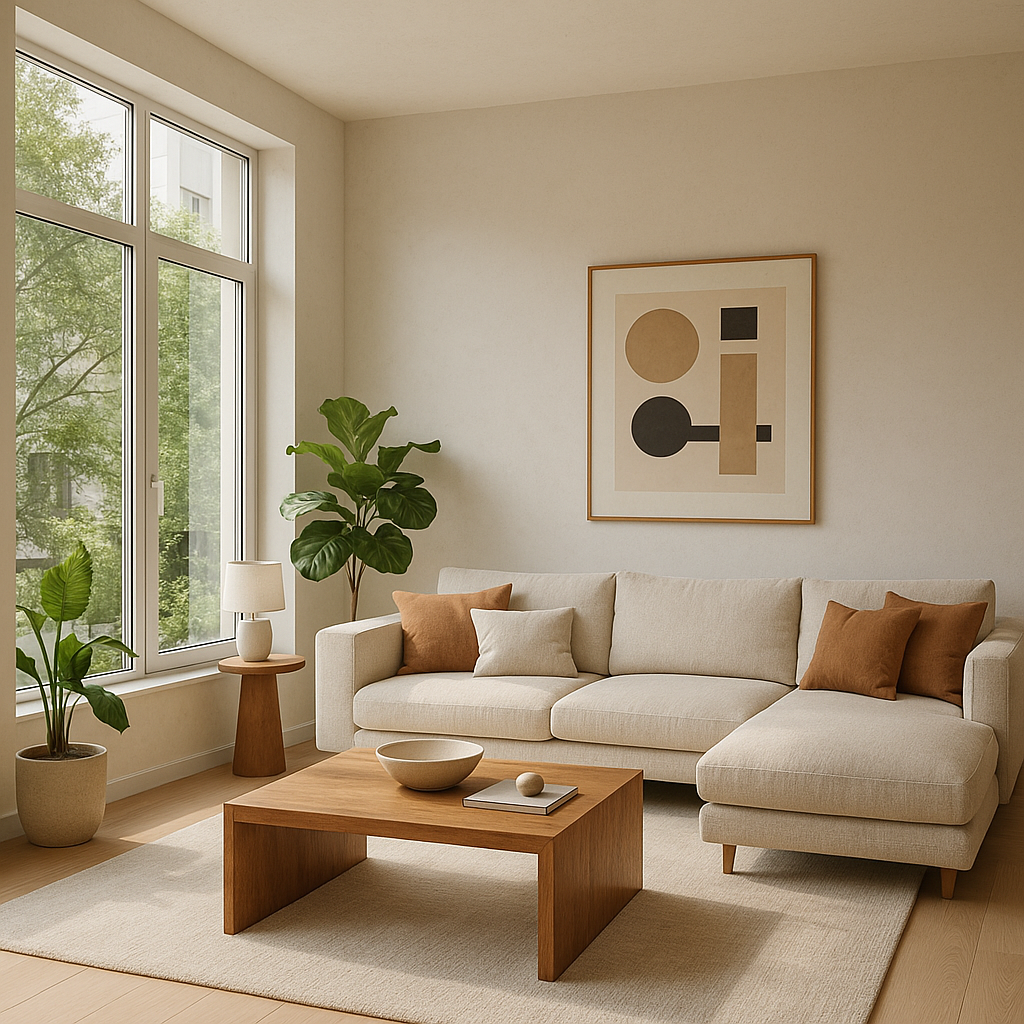

The following SQL uses the AI_CLASSIFY function to classify the image as a picture of a living area, kitchen, bath, garden, or master bedroom.
SELECT AI_CLASSIFY(TO_FILE('@my_images', 'REAL_ESTATE_STAGING.PNG'),
['Living Area', 'Kitchen', 'Bath', 'Garden', 'Master Bedroom']) AS room_classification;
Response:
{ "labels": [ "Living Area" ] }
The SQL below categorizes the objects found in the above image as a couch, window, table, television, or artwork.
SELECT AI_CLASSIFY (TO_FILE ('@my_images', 'REAL_ESTATE_STAGING.PNG'),
['Couch', 'Window', 'Table', 'Television', 'Art'], {'output_mode': 'multi'} )
AS living_room_objects;
Response:
{
"labels": [
"Art",
"Couch",
"Table",
"Window"
]
}
Search images¶
You can use AI_EMBED to find images that are similar to a target image. First, use the AI_EMBED function to generate an embedding vector for the target image, mapping its visual features into an abstract vector space, a numerical representation of the image’s features. You can then use vector similarity functions to compare this embedding vector to the embedding vectors of other images, producing a similarity score based on their common or similar visual features. This score can be used to classify, rank, or filter images based on their similarity to the target image.
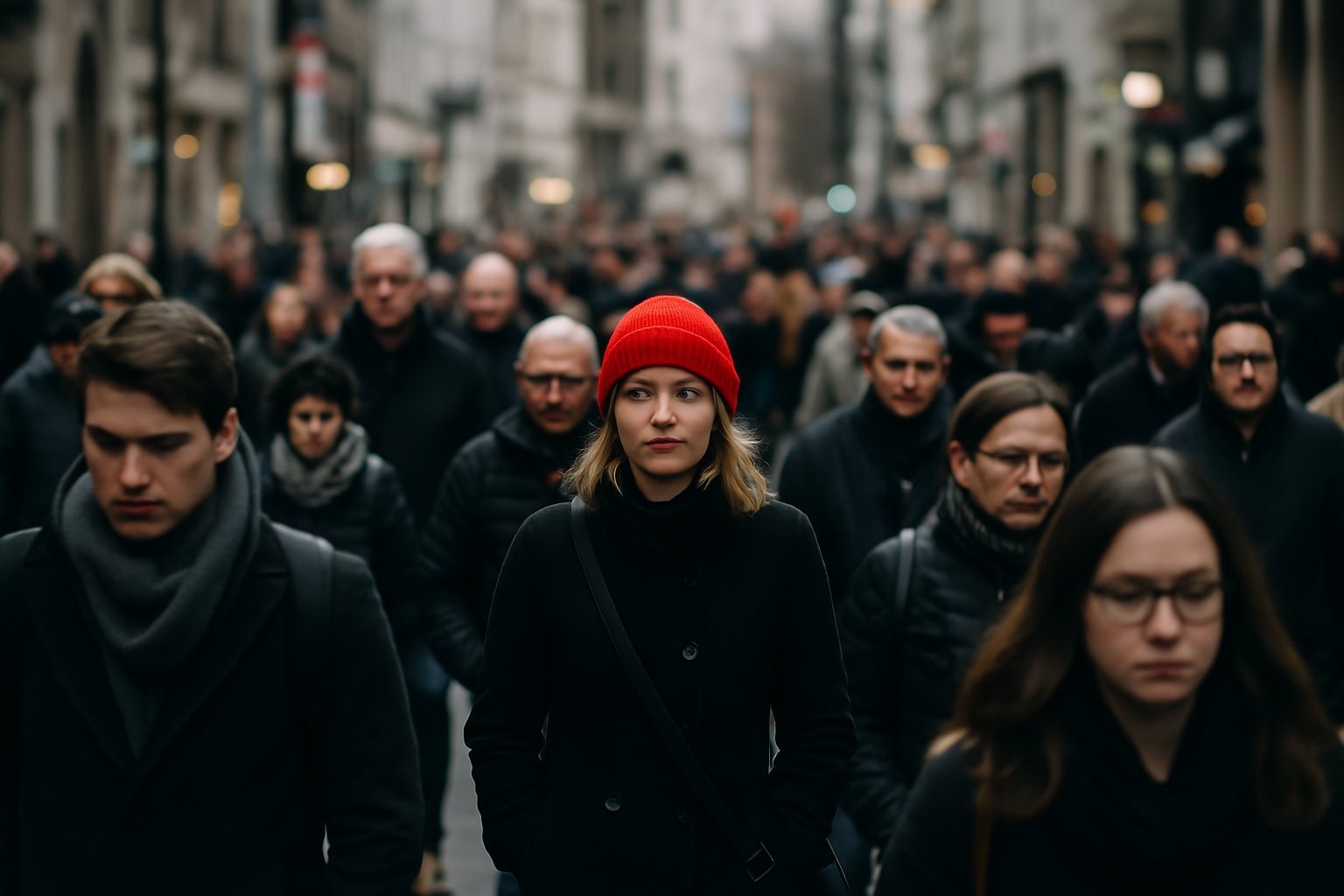

|
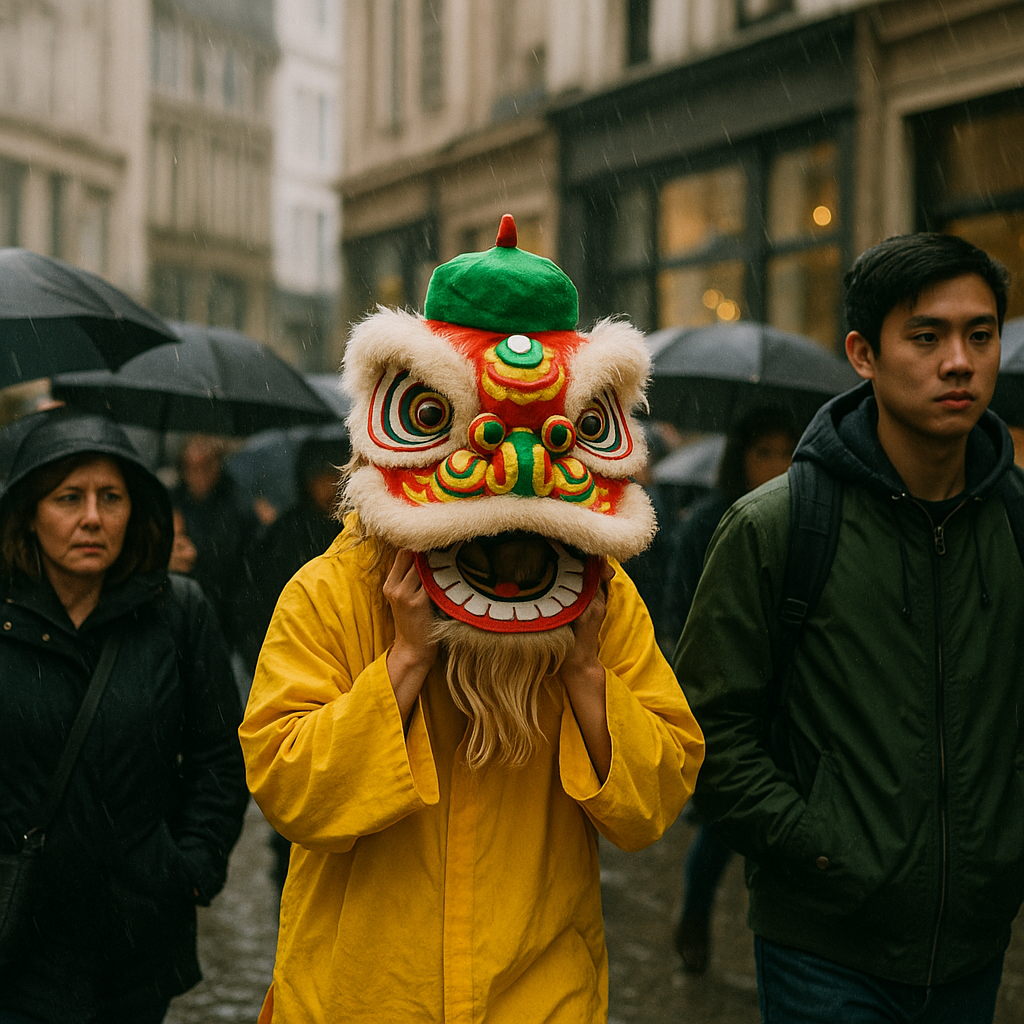

|
For example, given the images above, the following SQL generates an embedding vector for each image, then compares the vectors using cosine similarity. The result, about 0.5, indicates that the images are somewhat similar. Both photos are taken in an urban setting and contain background crowds, but the main subjects are different.
WITH ai_image_embeddings as (
SELECT
AI_EMBED('voyage-multimodal-3',
TO_FILE ('@my_images', 'CITY_WALKING1.PNG')) as image1_embeddings,
AI_EMBED('voyage-multimodal-3',
TO_FILE ('@my_images', 'CITY_WALKING2.PNG')) as image2_embeddings
)
SELECT VECTOR_COSINE_SIMILARITY(image1_embeddings,image2_embeddings) as similarity FROM ai_image_embeddings;
0.5359029029
To find images that are similar to a target image, you can use AI_SIMILARITY. The example below computes a similarity score for possibly thousands of images, and returns the advertising creatives that are most similar to the motorcycle advertisement below.
SELECT
TO_FILE('@ad_images', relative_path) as ALL_ADS
FROM DIRECTORY(@ad_images)
WHERE AI_SIMILARITY(TO_FILE('@ad_images', 'image_226.jpg'), ALL_ADS) >= 0.5;
The query returns images from a multimodal table where the similarity score is greater than 0.50. One of the images
identified (image_226.jpg) is the one we used as a reference.
+-----------------------------------------------------------+
| {} ALL_ADS |
+-----------------------------------------------------------+
| { "CONTENT_TYPE": "image/jpeg", |
| "ETAG": "686897696a7c876b7e", |
| "LAST_MODIFIED": "Wed, 26 Mar 2025 18:11:45 GMT", |
| "RELATIVE_PATH": "image_226.jpg", |
| "SIZE": 39086, |
| "STAGE": "@ad_images" } |
+-----------------------------------------------------------+
| { "CONTENT_TYPE": "image/jpeg", |
| "ETAG": "e7b678c7a696798686", |
| "LAST_MODIFIED": "Wed, 26 Mar 2025 18:11:57 GMT", |
| "RELATIVE_PATH": "image_441.jpg", |
| "SIZE": 12650, |
| "STAGE": "@ad_images" }, |
+-----------------------------------------------------------+
Model limitations¶
All models available to Snowflake Cortex have limitations on the total number of input and output tokens, known as the model’s context window. The context window size is measured in tokens. Inputs exceeding the context window limit result in an error. Output which would exceed the context window limit is truncated.
For text models, tokens generally represent approximately four characters of text, so the word count corresponding to a limit is less than the token count.
For image models, the token count per image depends on the vision model’s architecture. Tokens within a prompt (for example, “what animal is this?”) also contribute to the model’s context window.
Model |
Context window (tokens) |
File types |
File size |
Images per prompt |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1,047,576 |
.jpg, .jpeg, .png, .webp, .gif |
10MB |
5 |
|
1,047,576 |
.jpg, .jpeg, .png, .webp, .gif |
10MB |
5 |
|
200,000 |
.jpg, .jpeg, .png, .webp, .gif |
3.75 MB [L1] |
20 |
|
200,000 |
.jpg, .jpeg, .png, .webp, .gif |
3.75 MB [L1] |
20 |
|
200,000 |
.jpg, .jpeg, .png, .webp, .gif |
3.75 MB [L1] |
20 |
|
200,000 |
.jpg, .jpeg, .png, .webp, .gif |
3.75 MB [L1] |
20 |
|
128,000 |
.jpg, .jpeg, .png, .webp, .gif, .bmp |
10 MB |
10 |
|
128,000 |
.jpg, .jpeg, .png, .webp, .gif, .bmp |
10 MB |
10 |
|
128,000 |
.jpg, .jpeg, .png, .webp, .gif, .bmp |
10 MB |
1 |
|
32,768 |
.jpg, .png, .pg, .gif, .bmp |
10 MB |
1 |
Cost considerations¶
Billing scales with the number of tokens processed. The number of tokens per image depends on the architecture of the vision model.
Anthropic (
claude) models’ formula is roughly: tokens = (Width in pixels x Height in pixels) / 750.Mistral (
pixtral) models divide each image into batches of 16x16 pixels and converts each batch to a token. The total number of tokens is equivalent to roughly (Width in pixels / 16) * (Height in pixels / 16).Meta (
llama) models try to tile the image with square tiles. Depending on the image’s aspect ratio and size, the number of tiles can be up to 16, each represented by around 153 tokens.Open AI models rescale the image and tile it with square patches. For
openai-gpt-4.1, depending on the image ratio and size, the number of tokens can be 211 (images up to 512x512px), 352 (non-square images with longer side length 1024px), or from 630 tokens (square images at least 1024x1024px) to 913 tokens (non-square images with shorter side length 1024px). Foropenai-o4-mini, the rescaling logic is more involved, and the number of tokens varies from 86 (128x512px) to 1428 (2048x1024px), and does not follow a linear pattern.voyage-multimodal-3operates on an array of image patches that are roughly 14x14px in size. The image is rescaled so that it is covered by a grid, which has a minimum of 64 patches and a maximum of 2500 patches. Two extra image tokens are added, so the input ranges from 66 to 2502 tokens, depending on the image size and aspect ratio.
Note
The COUNT_TOKENS function does not currently support image inputs.
Choosing a vision model¶
The COMPLETE function supports multiple models of varying capability, latency, and cost. To achieve optimal performance per credit, choose a model that aligns with the content size and task complexity.
Model |
MMMU |
Mathvista |
ChartQA |
DocVQA |
VQAv2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
GPT-4o |
68.6 |
64.6 |
85.1 |
88.9 |
77.8 |
|
75.0 |
72.0 |
|||
|
81.6 |
84.3 |
|||
|
68.0 |
64.4 |
87.6 |
90.3 |
70.7 |
|
73.4 |
73.7 |
90 |
94.4 |
|
|
69.4 |
70.7 |
88.8 |
94.4 |
|
|
64.0 |
69.4 |
88.1 |
85.7 |
67 |
The benchmarks are:
MMMU: Evaluates multimodal models on multidisciplinary tasks that require college-level reasoning.
Mathvista: Mathematical reasoning benchmark within a visual context.
ChartQA: Evaluates complex reasoning questions about charts.
DocVQA and VQv2: Benchmarks for visual question-answering on documents.
For multimodal embeddings, only the voyage-multimodal-3 model is currently available. voyage-multimodal-3 is a
state-of-art multimodal embedding model capable of embedding text and images. It can extract key visual features from
sources such as screenshots of PDFs, slides, tables, and figures, reducing the need for complex document parsing
workflows. According to Voyage AI internal benchmarks, the voyage-multimodal-3 model outperforms competing models
such as OpenAI CLIP Large, Amazon Titan Multimodal, and Cohere Multimodal v3.
Regional availability¶
Support for this feature is available natively to accounts in the following Snowflake regions:
Model
|
AWS US West 2
(Oregon)
|
AWS US East 1
(N. Virginia)
|
AWS Europe Central 1
(Frankfurt)
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
✔ |
✔ |
|
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
|
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
|
✔ |
||
|
✔ |
||
|
AI_COMPLETE is available in additional regions through cross-region inference.
Error Conditions¶
Message |
Explanation |
|---|---|
Request failed for external function SYSTEM$COMPLETE_WITH_IMAGE_INTERNAL with remote service error: 400 ‘“invalid image path” |
Either the file extension or the file itself is not accepted by the model. The message might also mean that the file path is incorrect; that is, the file does not exist at the specified location. Filenames are case-sensitive. |
Error in secure object |
May indicate that the stage does not exist. Check the stage name and ensure that the stage exists and is accessible. Be sure
to use the at (@) sign at the beginning of the stage path, such as |
Request failed for external function _COMPLETE_WITH_PROMPT with remote service error: 400 ‘“invalid request parameters: unsupported image format: image/** |
Unsupported image format given to |
Request failed for external function _COMPLETE_WITH_PROMPT with remote service error: 400 ‘“invalid request parameters: Image data exceeds the limit of 5.00 MB” |
The provided image given to |
Legal¶
The data classification of inputs and outputs are as set forth in the following table.
Input data classification |
Output data classification |
Designation |
|---|---|---|
Usage Data |
Customer Data |
Generally available functions are Covered AI Features. Preview functions are Preview AI Features. [1] |
For additional information, refer to Snowflake AI and ML.
